vuex基础-介绍
为什么会有Vuex ?
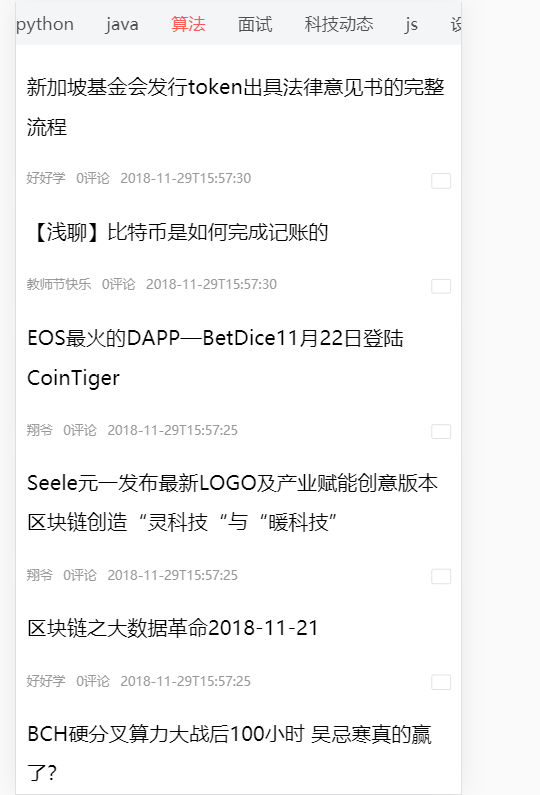
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用**集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测**的方式发生变化。
- vuex是采用集中式管理组件依赖的共享数据的一个工具,可以解决不同组件数据共享问题。
结论
- 修改state状态必须通过**
mutations**
- **
mutations**只能执行同步代码,类似ajax,定时器之类的代码不能在mutations中执行
- 执行异步代码,要通过actions,然后将数据提交给mutations才可以完成
- state的状态即共享数据可以在组件中引用
- 组件中可以调用action
vuex基础-初始化功能
建立一个新的脚手架项目, 在项目中应用vuex
开始vuex的初始化建立,选择模式时,选择默认模式
初始化:
- 第一步:
npm i vuex --save => 安装到**运行时依赖** => 项目上线之后依然使用的依赖 ,开发时依赖 => 开发调试时使用
开发时依赖 就是开开发的时候,需要的依赖,运行时依赖,项目上线运行时依然需要的
- 第二步:在main.js中
import Vuex from 'vuex'
- 第三步:在main.js中
Vue.use(Vuex) => 调用了 vuex中的 一个install方法
- 第四步:
const store = new Vuex.Store({...配置项})
- 第五步:在根实例配置 store 选项指向 store 实例对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store
})
|
vuex基础-state
state是放置所有公共状态的属性,如果你有一个公共状态数据 , 你只需要定义在 state对象中
定义state
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}
})
|
如何在组件中获取count?
原始形式- 插值表达式
App.vue
组件中可以使用 this.$store 获取到vuex中的store对象实例,可通过state属性属性获取count, 如下
1
| <div> state的数据:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
|
计算属性 - 将state属性定义在计算属性中
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
|
1
| <div> state的数据:{{ count }}</div>
|
辅助函数 - mapState
mapState是辅助函数,帮助我们把store中的数据映射到 组件的计算属性中, 它属于一种方便用法
用法 : 第一步:导入mapState
1
| import { mapState } from 'vuex'
|
第二步:采用数组形式引入state属性
上面代码的最终得到的是 类似
1
2
3
| count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
|
第三步:利用延展运算符将导出的状态映射给计算属性
1
2
3
| computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
}
|
1
| <div> state的数据:{{ count }}</div>
|
vuex基础-mutations
state数据的修改只能通过mutations,并且mutations必须是同步更新,目的是形成**数据快照**
数据快照:一次mutation的执行,立刻得到一种视图状态,因为是立刻,所以必须是同步
定义mutations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
}
})
|
格式说明
mutations是一个对象,对象中存放修改state的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| mutations: {
addCount (state) {
state.count += 1
}
},
|
如何在组件中调用mutations
原始形式-$store
新建组件child-a.vue,内容为一个button按钮,点击按钮调用mutations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <template>
<button @click="addCount">+1</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
// 调用方法
addCount () {
// 调用store中的mutations 提交给muations
// commit('muations名称', 2)
this.$store.commit('addCount', 10) // 直接调用mutations
}
}
}
</script>
|
带参数的传递
1
2
3
4
| addCount (state, payload) {
state.count += payload
}
this.$store.commit('addCount', 10)
|
辅助函数 - mapMutations
mapMutations和mapState很像,它把位于mutations中的方法提取了出来,我们可以将它导入
1
2
3
4
| import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapMutations(['addCount'])
}
|
上面代码的含义是将mutations的方法导入了methods中,等同于
1
2
3
4
5
6
| methods: {
addCount () {
this.$store.commit('addCount')
}
}
|
此时,就可以直接通过this.addCount调用了
1
| <button @click="addCount(100)">+100</button>
|
但是请注意: Vuex中mutations中要求不能写异步代码,如果有异步的ajax请求,应该放置在actions中
vuex基础-actions
state是存放数据的,mutations是同步更新数据,actions则负责进行异步操作
定义actions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| actions: {
getAsyncCount (context) {
setTimeout(function(){
context.commit('addCount', 123)
}, 1000)
}
}
|
原始调用 - $store
1
2
3
| addAsyncCount () {
this.$store.dispatch('getAsyncCount')
}
|
传参调用
1
2
3
| addAsyncCount () {
this.$store.dispatch('getAsyncCount', 123)
}
|
辅助函数 -mapActions
actions也有辅助函数,可以将action导入到组件中
1
2
3
4
| import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapActions(['getAsyncCount'])
}
|
直接通过 this.方法就可以调用
1
| <button @click="getAsyncCount(111)">+异步</button>
|
vuex基础-getters
除了state之外,有时我们还需要从state中派生出一些状态,这些状态是依赖state的,此时会用到getters
例如,state中定义了list,为1-10的数组,
1
2
3
| state: {
list: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
}
|
组件中,需要显示所有大于5的数据,正常的方式,是需要list在组件中进行再一步的处理,但是getters可以帮助我们实现它
定义getters
1
2
3
4
5
| getters: {
filterList: state => state.list.filter(item => item > 5)
}
|
使用getters
原始方式 -$store
1
| <div>{{ $store.getters.filterList }}</div>
|
辅助函数 - mapGetters
1
2
3
| computed: {
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
}
|
1
| <div>{{ filterList }}</div>
|
Vuex中的模块化-Module
为什么会有模块化?
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
这句话的意思是,如果把所有的状态都放在state中,当项目变得越来越大的时候,Vuex会变得越来越难以维护
由此,又有了Vuex的模块化
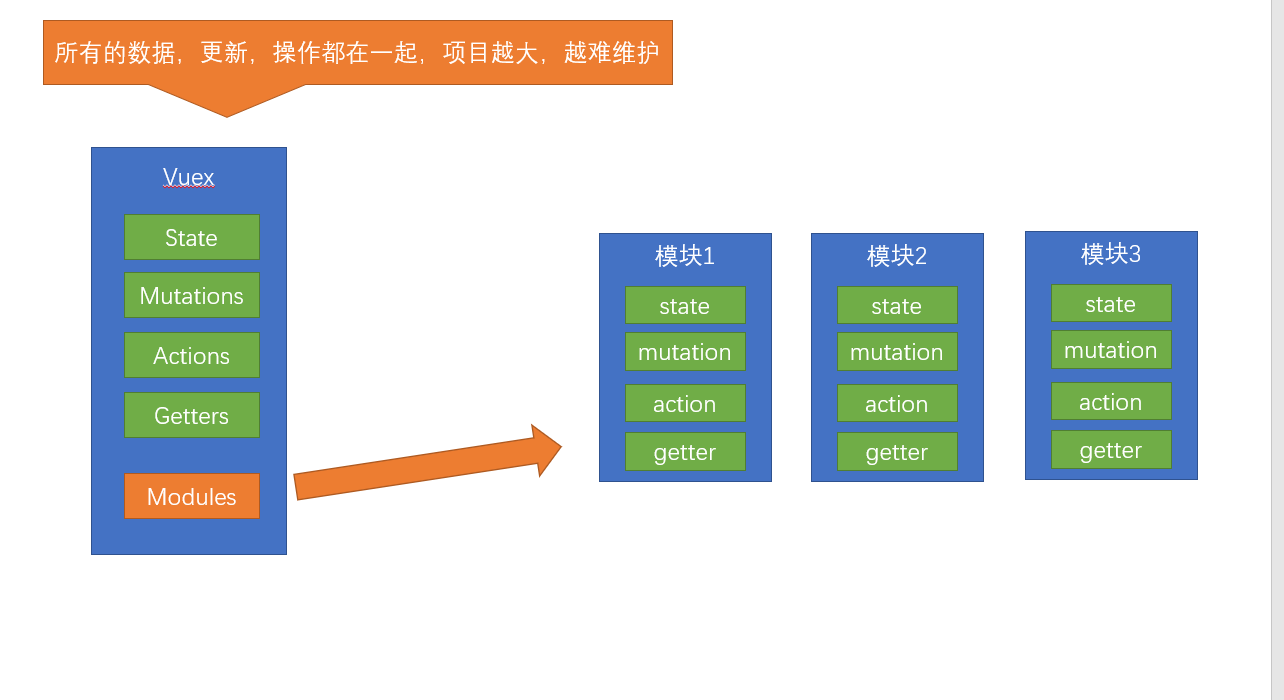
模块化的简单应用
应用
定义两个模块 user 和 setting
user中管理用户的状态 token
setting中管理 应用的名称 name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
user: {
state: {
token: '12345'
}
},
setting: {
state: {
name: 'Vuex实例'
}
}
})
|
定义child-b组件,分别显示用户的token和应用名称name
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <template>
<div>
<div>用户token {{ $store.state.user.token }}</div>
<div>网站名称 {{ $store.state.setting.name }}</div>
</div>
</template>
|
请注意: 此时要获取子模块的状态 需要通过 $store.state.模块名称.属性名 来获取
看着获取有点麻烦,我们可以通过之前学过的getters来改变一下
1
2
3
4
| getters: {
token: state => state.user.token,
name: state => state.setting.name
}
|
请注意:这个getters是根级别的getters哦
通过mapGetters引用
1
2
3
| computed: {
...mapGetters(['token', 'name'])
}
|
模块化中的命名空间
命名空间 namespaced
这里注意理解
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation 或 action 作出响应。
这句话的意思是 刚才的user模块还是setting模块,它的 action、mutation 和 getter 其实并没有区分,都可以直接通过全局的方式调用 如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| user: {
state: {
token: '12345'
},
mutations: {
updateToken (state) {
state.token = 678910
}
}
},
|
通过mapMutations调用
1
2
3
4
| methods: {
...mapMutations(['updateToken'])
}
<button @click="updateToken">修改token</button>
|
但是,如果我们想保证内部模块的高封闭性,我们可以采用namespaced来进行设置
高封闭性?可以理解成 一家人如果分家了,此时,你的爸妈可以随意的进出分给你的小家,你觉得自己没什么隐私了,我们可以给自己的房门加一道锁(命名空间 namespaced),你的父母再也不能进出你的小家了
如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| user: {
namespaced: true,
state: {
token: '12345'
},
mutations: {
updateToken (state) {
state.token = 678910
}
}
},
|
使用带命名空间的模块 action/mutations
方案1:直接调用-带上模块的属性名路径
1
2
3
| test () {
this.$store.dispatch('user/updateToken')
}
|
方案2:辅助函数-带上模块的属性名路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| methods: {
...mapMutations(['user/updateToken']),
test () {
this['user/updateToken']()
}
}
<button @click="test">修改token</button>
|
方案3: createNamespacedHelpers 创建基于某个命名空间辅助函数
1
2
3
| import { mapGetters, createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapMutations } = createNamespacedHelpers('user')
<button @click="updateToken">修改token2</button>
|
关于Vuex的更多用法,后续在项目中讲解
vuex案例-搭建黑马头条项目
接下来,通过一个案例来使用Vuex介入我们的数据管理
通过vue-cli脚手架搭建项目
选择 vuex / eslint(stanadard) / pre-cssprocesser (less) 确定
在main.js中引入样式(该样式在资源/vuex样式中,拷贝到styles目录下)
1
| import './styles/index.css'
|
拷贝图片资源到assets目录下(在资源/vuex样式目录下的图片)
在App.vue中拷贝基本结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| <div id="app">
<ul class="catagtory">
<li class='select'>开发者资讯</li>
<li>ios</li>
<li>c++</li>
<li>android</li>
<li>css</li>
<li>数据库</li>
<li>区块链</li>
<li>go</li>
<li>产品</li>
<li>后端</li>
<li>linux</li>
<li>人工智能</li>
<li>php</li>
<li>javascript</li>
<li>架构</li>
<li>前端</li>
<li>python</li>
<li>java</li>
<li>算法</li>
<li>面试</li>
<li>科技动态</li>
<li>js</li>
<li>设计</li>
<li>数码产品</li>
<li>html</li>
<li>软件测试</li>
<li>测试开发</li>
</ul>
<div class="list">
<div class="article_item">
<h3 class="van-ellipsis">python数据预处理 :数据标准化</h3>
<div class="img_box">
<img src="@/assets/back.jpg"
class="w100" />
</div>
<!---->
<div class="info_box">
<span>13552285417</span>
<span>0评论</span>
<span>2018-11-29T17:02:09</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
|
vuex案例-封装分类组件和频道组件
为了更好的区分组件之间的职责,我们将上方的频道和下方的列表封装成不同的组件
components/catagtory.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| <template>
<ul class="catagtory">
<li class='select'>开发者资讯</li>
<li>ios</li>
<li>c++</li>
<li>android</li>
<li>css</li>
<li>数据库</li>
<li>区块链</li>
<li>go</li>
<li>产品</li>
<li>后端</li>
<li>linux</li>
<li>人工智能</li>
<li>php</li>
<li>javascript</li>
<li>架构</li>
<li>前端</li>
<li>python</li>
<li>java</li>
<li>算法</li>
<li>面试</li>
<li>科技动态</li>
<li>js</li>
<li>设计</li>
<li>数码产品</li>
<li>html</li>
<li>软件测试</li>
<li>测试开发</li>
</ul>
</template>
|
components/new-list.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <template>
<div class="list">
<div class="article_item">
<h3 class="van-ellipsis">python数据预处理 :数据标准化</h3>
<div class="img_box">
<img src="@/assets/back.jpg"
class="w100" />
</div>
<!---->
<div class="info_box">
<span>13552285417</span>
<span>0评论</span>
<span>2018-11-29T17:02:09</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
|
在App.vue中引入并使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <template>
<!-- app.vue是根组件 -->
<div id="app">
<catagtory />
<new-list />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Catagtory from './components/catagtory'
import NewList from './components/new-list'
export default {
components: {
Catagtory, NewList
}
}
</script>
|
vuex案例-在vuex中加载分类和频道数据
设计categtory和newlist的vuex模块
安装请求数据的工具 axios
接口
获取频道列表
http://ttapi.research.itcast.cn/app/v1_0/channels
获取频道头条
http://ttapi.research.itcast.cn/app/v1_1/articles?channel_id=频道id×tamp=时间戳&with_top=1
我们采用模块化的管理模式,建立一个专门的模块来管理分类和新闻数据
在store目录下新建目录modules, 新建 catagtory.js和newlist.js
模块结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
| export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {}
}
|
在store/index.js中引入定义的两个模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import catagtory from './modules/catagtory'
import newlist from './modules/newlist'
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
catagtory,
newlist
}
})
|
分类模块下设置分类数组和当前激活分类
在catagtory的 state中定义分类频道列表和当前激活
1
2
3
4
| state: {
catagtory: [],
currentCatagtory: ''
}
|
定义更新频道列表的mutations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| mutations: {
updateCatagtory (state, payload) {
state.catagtory = payload
},
updateCurrentCatagtory (state, payload) {
state.currentCatagtory = payload
}
}
|
通过getters建立对于分类数据和当前分类的快捷访问
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
catagtory,
newlist
},
getters: {
catagtory: state => state.catagtory.catagtory,
currentCatagtory: state => state.catagtory.currentCatagtory
}
})
|
遍历分类数据并判断激活class
分类组件遍历vuex数据
1
2
3
4
| import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['catagtory', 'currentCatagtroy'])
},
|
1
2
3
| <ul class="catagtory">
<li :class="{ select: currentCatagtory === item.id }" v-for="item in catagtory" :key="item.id">{{ item.name }}</li>
</ul>
|
封装调用获取分类action,激活第一个分类
定义获取频道列表的action, 将第一个频道激活
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| actions: {
async getCatagtory (context) {
const { data: { data: { channels } } } = await axios.get('http://ttapi.research.itcast.cn/app/v1_0/channels')
context.commit('updateCatagtory', channels)
context.commit('updateCurrentCatagtory', channels[0].id)
}
}
|
初始化catagtory时调用action
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['catagtory'])
},
created () {
this.$store.dispatch('catagtory/getCatagtory')
}
}
|
点击分类时,触发分类切换
1
2
| <li @click="$store.commit('catagtory/updateCurrentCatagtory', item.id)" :class="{ select: currentCatagtroy === item.id }" v-for="item in catagtory" :key="item.id">{{ item.name }}</li>
|
定义新闻数据,并封装获取新闻的Action
在newlist.js中定义获取头条内容的数据
定义更新头条内容的mutations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| mutations: {
updateList (state, { currentCatagtory, list }) {
state.allData = { ...state.allData, [currentCatagtory]: list }
}
},
|
定义根据分类标识获取新闻的action
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| actions: {
async getNewList (context, cataId) {
const { data: { data: { results } } } = await axios.get(`http://ttapi.research.itcast.cn/app/v1_1/articles?channel_id=${cataId}×tamp=${Date.now()}&with_top=1`)
context.commit('updateList', { currentCatagtory: cataId, list: results })
}
}
|
监听激活分类,触发获取新闻Action
在new-list组件中,引入当前分类的id,监视其改变,一旦改变,触发获取新闻的action
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['currentCatagtroy'])
},
watch: {
currentCatagtory (newValue) {
this.$store.dispatch('newlist/getNewList', newValue)
}
}
}
|
处理显示新闻内容的数据
定义当前显示列表的getters
1
2
3
| getters: {
currentList: state => state.newlist.allData[state.catagtory.currentCatagtory] || []
}
|
修改new-list内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| <template>
<div class="list">
<div class="article_item" v-for="item in currentList" :key="item.art_id">
<h3 class="van-ellipsis">{{ item.title }}</h3>
<div class="img_box" v-if="item.cover.type === 1">
<img :src="item.cover.images[0]"
class="w100" />
</div>
<div class="img_box" v-else-if="item.cover.type === 3">
<img :src="item.cover.images[0]"
class="w33" />
<img :src="item.cover.images[1]"
class="w33" />
<img :src="item.cover.images[2]"
class="w33" />
</div>
<!---->
<div class="info_box">
<span>{{ item.aut_name }}</span>
<span>{{ item.comm_count }}评论</span>
<span>{{ item.pubdate }}</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入当前激活的分类id
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['currentCatagtory', 'currentList'])
},
watch: {
currentCatagtory (newValue) {
// newValue是当前最新的激活的id
this.$store.dispatch('newlist/getNewList', newValue)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
|