0.学习目标
- 利用MQ实现数据同步
- 会使用SpringDataRedis
- 会使用阿里短信SDK发送短信
1.实现数据同步
昨天的学习中,我们已经完成了对MQ的基本学习和认识。接下来,我们就改造项目,实现搜索服务、商品静态页的数据同步。
1.1.思路分析
发送方:商品微服务
接收方:搜索微服务、静态页微服务
在ly-common中编写一个常量类,记录将来会用到的Exchange名称、Queue名称、routing_key名称
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| package com.leyou.common.constants;
public abstract class MQConstants {
public static final class Exchange {
public static final String ITEM_EXCHANGE_NAME = "ly.item.exchange";
}
public static final class RoutingKey {
public static final String ITEM_UP_KEY = "item.up";
public static final String ITEM_DOWN_KEY = "item.down";
}
public static final class Queue{
public static final String SEARCH_ITEM_UP = "search.item.up.queue";
public static final String SEARCH_ITEM_DOWN = "search.item.down.queue";
public static final String PAGE_ITEM_UP = "page.item.up.queue";
public static final String PAGE_ITEM_DOWN = "page.item.down.queue";
}
}
|
1.2.发送消息
我们先在商品微服务ly-item-service中实现发送消息。
1.2.1.引入依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
1.2.2.配置文件
我们在application.yml中添加一些有关RabbitMQ的配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.206.66
username: leyou
password: leyou
virtual-host: /leyou
template:
retry:
enabled: true
initial-interval: 10000ms
max-interval: 80000ms
multiplier: 2
publisher-confirms: true
|
- template:有关
AmqpTemplate的配置
- retry:失败重试
- enabled:开启失败重试
- initial-interval:第一次重试的间隔时长
- max-interval:最长重试间隔,超过这个间隔将不再重试
- multiplier:下次重试间隔的倍数,此处是2即下次重试间隔是上次的2倍
- exchange:缺省的交换机名称,此处配置后,发送消息如果不指定交换机就会使用这个
- publisher-confirms:生产者确认机制,确保消息会正确发送,如果发送失败会有错误回执,从而触发重试
1.2.3.Json消息转换器
需要注意的是,默认情况下,AMQP会使用JDK的序列化方式进行处理,传输数据比较大,效率太低。我们可以自定义消息转换器,使用JSON来处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}
|
位置:
1.2.3.改造GoodsService
改造GoodsService中的商品上下架功能,发送消息,注意用静态导入方式,导入在ly-common中定义的常量:
//TODO 拓展其他功能,比如,新增,修改,删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.RoutingKey.*;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Exchange.*;
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Transactional
public void updateSaleable(Long id, Boolean saleable) {
Spu spu = new Spu();
spu.setId(id);
spu.setSaleable(saleable);
int count = spuMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(spu);
if (count != 1) {
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.UPDATE_OPERATION_FAIL);
}
Example example = new Example(Sku.class);
example.createCriteria().andEqualTo("spuId", id);
Sku sku = new Sku();
sku.setEnable(saleable);
skuMapper.updateByExampleSelective(sku, example);
String key = saleable ? ITEM_UP_KEY : ITEM_DOWN_KEY;
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(ITEM_EXCHANGE_NAME,key, id);
}
|
1.3.搜索服务接收消息
搜索服务接收到消息后要做的事情:
我们需要两个不同队列,监听不同类型消息。
1.3.1.引入依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
1.3.2.添加配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
| spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.206.66
username: leyou
password: leyou
virtual-host: /leyou
|
这里只是接收消息而不发送,所以不用配置template相关内容。
不过,不要忘了消息转换器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}
|
1.3.3.编写监听器
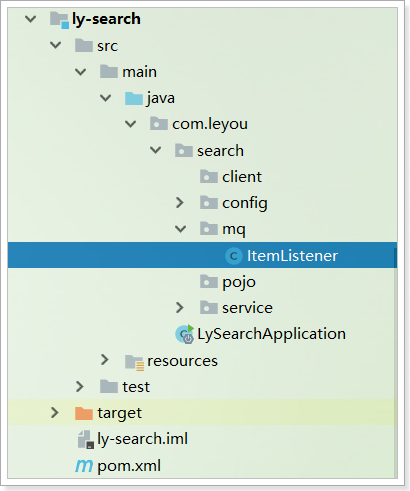
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| package com.leyou.search.mq;
import com.leyou.search.service.SearchService;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Exchange.*;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Queue.*;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.RoutingKey.*;
@Component
public class ItemListener {
@Autowired
private SearchService searchService;
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = SEARCH_ITEM_UP, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(
name = ITEM_EXCHANGE_NAME, type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = ITEM_UP_KEY
))
public void listenInsert(Long id){
if(id != null){
searchService.createIndex(id);
}
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = SEARCH_ITEM_DOWN, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(
name = ITEM_EXCHANGE_NAME, type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = ITEM_DOWN_KEY
))
public void listenDelete(Long id){
if(id != null){
searchService.deleteById(id);
}
}
}
|
1.3.4.编写创建和删除索引方法
这里因为要创建和删除索引,我们需要在SearchService中拓展两个方法,创建和删除索引:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public void createIndex(Long id){
SpuDTO spu = itemClient.querySpuById(id);
Goods goods = buildGoods(spu);
goodsRepository.save(goods);
}
public void deleteById(Long id) {
goodsRepository.deleteById(id);
}
|
创建索引的方法可以从之前导入数据的测试类中拷贝和改造。
1.4.静态页服务接收消息
商品静态页服务接收到消息后的处理:
与前面搜索服务类似,也需要两个队列来处理。
1.4.1.引入依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
1.4.2.添加配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
| spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.206.66
username: leyou
password: leyou
virtual-host: /leyou
|
这里只是接收消息而不发送,所以不用配置template相关内容。
不过,不要忘了消息转换器:
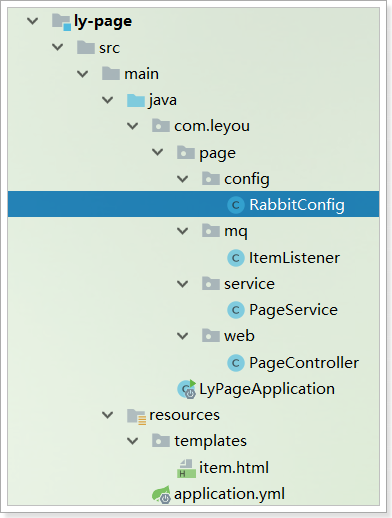
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}
|
1.4.3.编写监听器
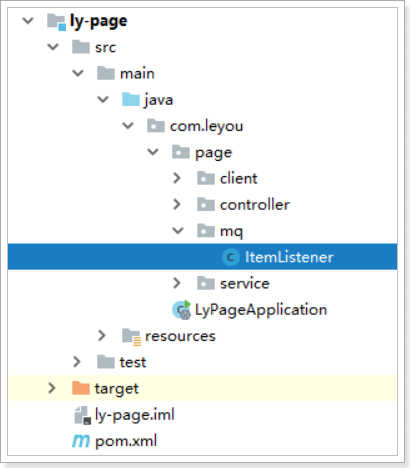
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| package com.leyou.page.mq;
import com.leyou.page.service.PageService;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Exchange.*;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Queue.*;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.RoutingKey.*;
@Component
public class ItemListener {
@Autowired
private PageService pageService;
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = PAGE_ITEM_UP, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(
name = ITEM_EXCHANGE_NAME, type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = ITEM_UP_KEY
))
public void listenInsert(Long id) {
if (id != null) {
pageService.createItemHtml(id);
}
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = PAGE_ITEM_DOWN, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(
name = ITEM_EXCHANGE_NAME, type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = ITEM_DOWN_KEY
))
public void listenDelete(Long id) {
if (id != null) {
pageService.deleteItemHtml(id);
}
}
}
|
1.4.4.添加删除页面方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public void deleteItemHtml(Long id) {
File file = new File(itemDir, id + ".html");
if(file.exists()){
if (!file.delete()) {
log.error("【静态页服务】静态页删除失败,商品id:{}", id);
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.FILE_WRITER_ERROR);
}
}
}
|
1.5.测试
查看RabbitMQ控制台
重新启动项目,并且登录RabbitMQ管理界面:http://192.168.206.66:15672
可以看到,交换机已经创建出来了:
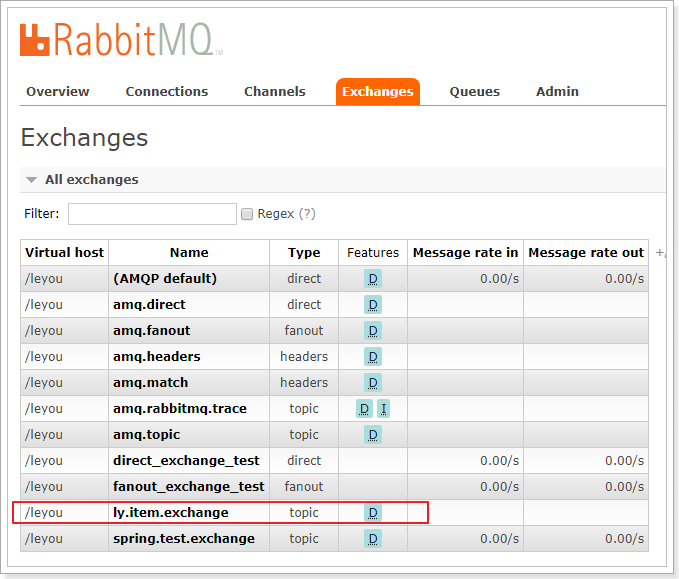
队列也已经创建完毕:
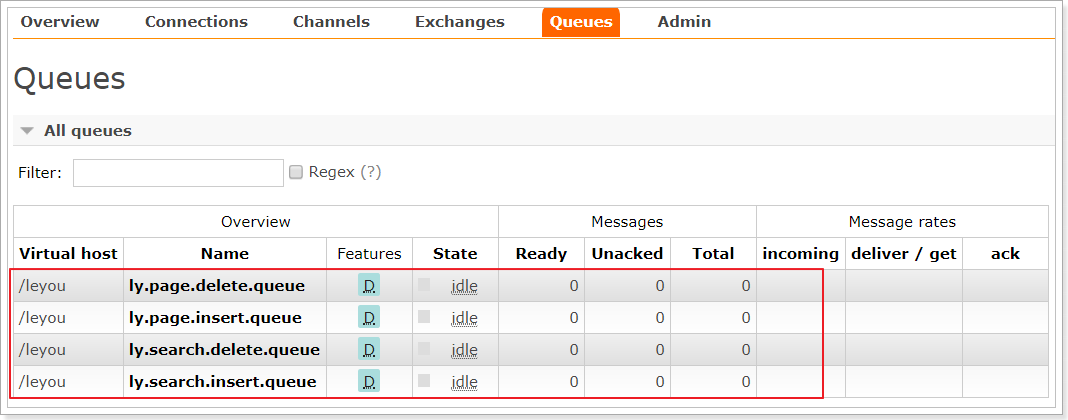
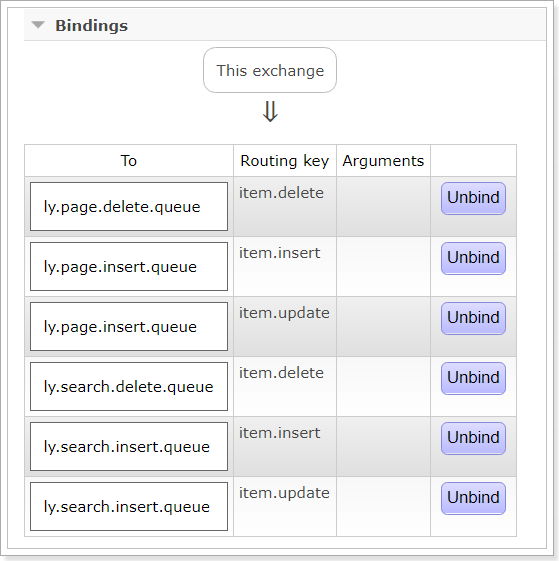
并且队列都已经绑定到交换机:
查看数据
我们搜索下手机:

商品详情页:

修改商品
然后在管理后台修改商品:
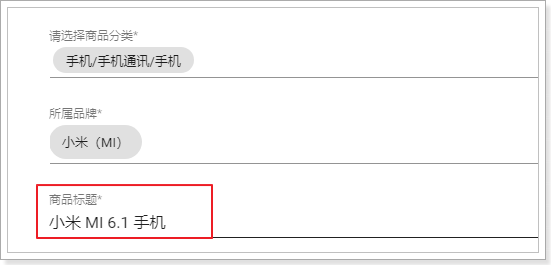
我们修改以下内容:
标题改成6.1
商品详情加点文字:

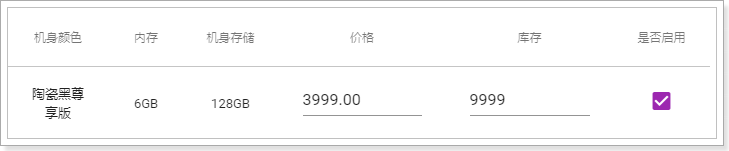
价格改为3999
再次查看数据
搜索页:
详情页:

详情内容:
完美!
2.Redis回顾
完成了商品的详情展示,下一步自然是购物了。不过购物之前要完成用户的注册和登录等业务,我们需要使用到Redis技术,一起来回顾下。
2.1.NoSql
Redis是目前非常流行的一款NoSql数据库。
什么是NoSql?

常见的NoSql产品:

2.2.Redis的介绍和安装
2.2.1.简介
Redis的网址:
官网:速度很慢,几乎进去不去啊。
中文网站:有部分翻译的官方文档,英文差的同学的福音
历史:

特性:
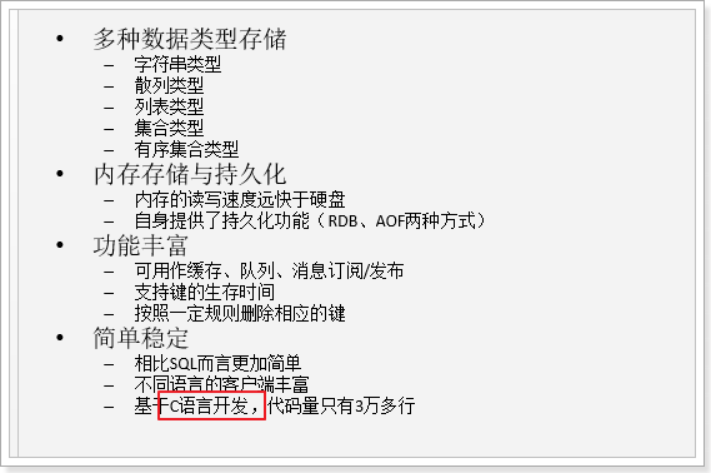
2.2.2.Redis与Memcache
Redis和Memcache是目前非常流行的两种NoSql数据库,读可以用于服务端缓存。两者有怎样的差异呢?
从实现来看:
从存储方式来看:
- redis:支持数据持久化和主从备份,数据更安全
- Memcache:数据存于内存,没有持久化功能
从功能来看:
- redis:除了基本的k-v 结构外,支持多种其它复杂结构、事务等高级功能
- Memcache:只支持基本k-v 结构
从可用性看:
- redis:支持主从备份、数据分片、哨兵监控
- memcache:没有分片功能,需要从客户端支持
可以看出,Redis相比Memcache功能更加强大,支持的数据结构也比较丰富,已经不仅仅是一个缓存服务。而Memcache的功能相对单一。
一些面试问题:Redis缓存击穿问题、缓存雪崩问题。
2.2.3.安装
参考课前资料中的:《redis安装配置.md》
2.3.Redis指令
通过help命令可以让我们查看到Redis的指令帮助信息:
在help后面跟上空格,然后按tab键,会看到Redis对命令分组的组名:
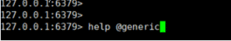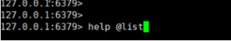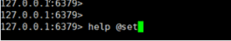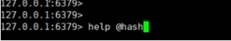
主要包含:
- @generic:通用指令
- @string:字符串类型指令
- @list:队列结构指令
- @set:set结构指令
- @sorted_set:可排序的set结构指令
- @hash:hash结构指令
其中除了@generic以为的,对应了Redis中常用的5种数据类型:
- String:等同于java中的,
Map<String,String>
- list:等同于java中的
Map<String,List<String>>
- set:等同于java中的
Map<String,Set<String>>
- sort_set:可排序的set
- hash:等同于java中的:
Map<String,Map<String,String>>
可见,Redis中存储数据结构都是类似java的map类型。Redis不同数据类型,只是'map'的值的类型不同。
2.3.1.通用指令
keys
获取符合规则的键名列表。
语法:keys pattern
示例:keys * (查询所有的键)
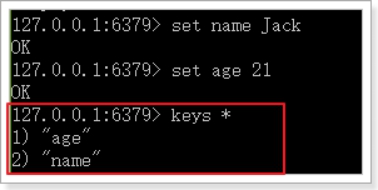
这里的pattern其实是正则表达式,所以语法基本是类似的
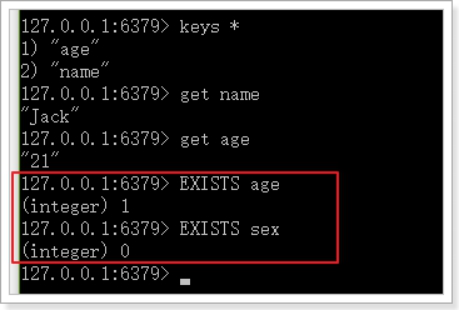
exists
判断一个键是否存在,如果存在返回整数1,否则返回0
语法:EXISTS key
示例:
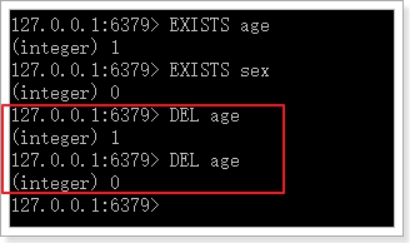
del
DEL:删除key,可以删除一个或多个key,返回值是删除的key的个数。
语法:DEL key [key … ]
示例:
expire
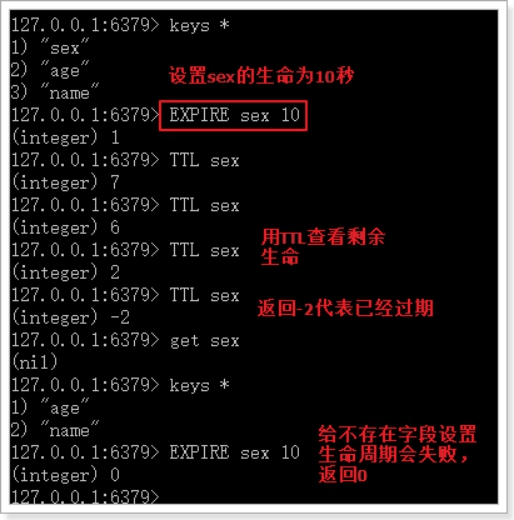
TTL
TTL:查看一个key的过期时间
语法:TTL key
返回值:
- 返回剩余的过期时间
- -1:永不过期
- -2:已过期或不存在
示例:
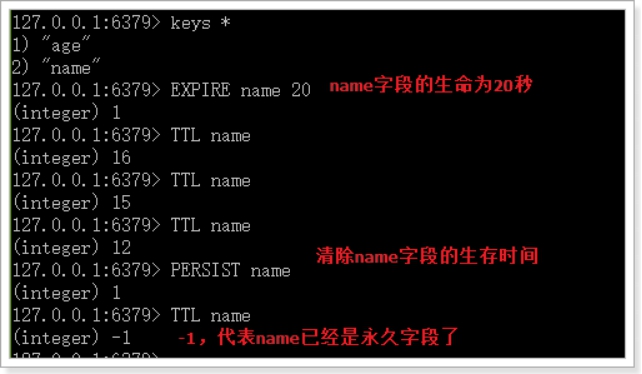
persist
2.3.2.字符串指令
字符串结构,其实是Redis中最基础的K-V结构。其键和值都是字符串。类似Java的Map<String,String>

常用指令:
2.3.3.hash结构命令
Redis的Hash结构类似于Java中的Map<String,Map<String,Stgring>>,键是字符串,值是另一个映射。结构如图:
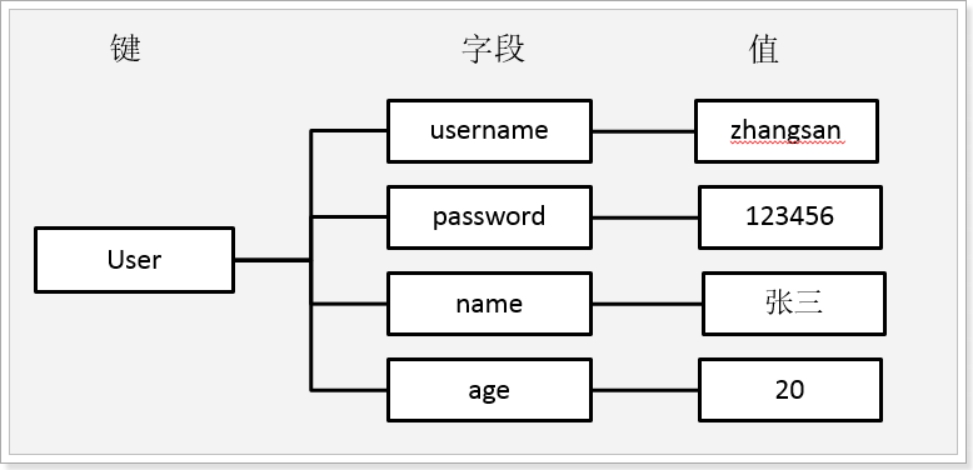
这里我们称键为key,字段名为 hKey, 字段值为 hValue
常用指令:
HSET、HSETNX和HGET(添加、获取)
HSET
介绍:
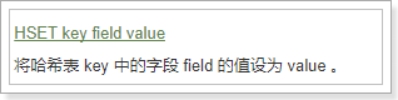
- Redis Hset 命令用于为哈希表中的字段赋值 。
- 如果哈希表不存在,一个新的哈希表被创建并进行 HSET 操作。
- 如果字段已经存在于哈希表中,旧值将被覆盖。
返回值:
- 如果字段是哈希表中的一个新建字段,并且值设置成功,返回 1 。
- 如果哈希表中域字段已经存在且旧值已被新值覆盖,返回 0
示例:

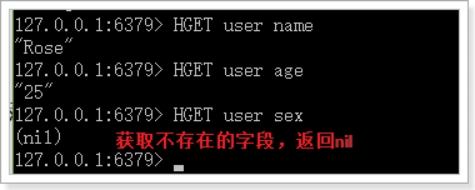
HGET
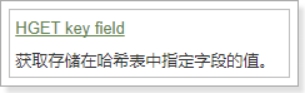
Hget 命令用于返回哈希表中指定字段的值。
HGETALL
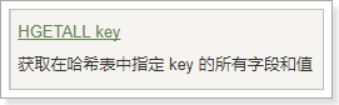
指定key 的所有字段的名及值。返回值里,紧跟每个字段名(field name)之后是字段的值(value),所以返回值的长度是哈希表大小的两倍
示例:
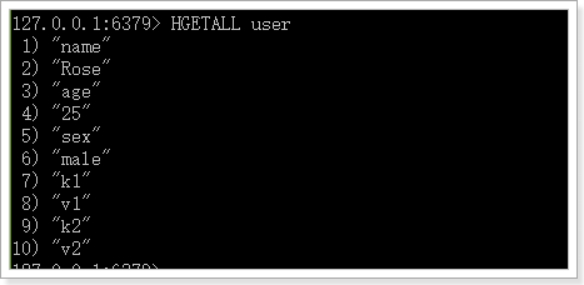
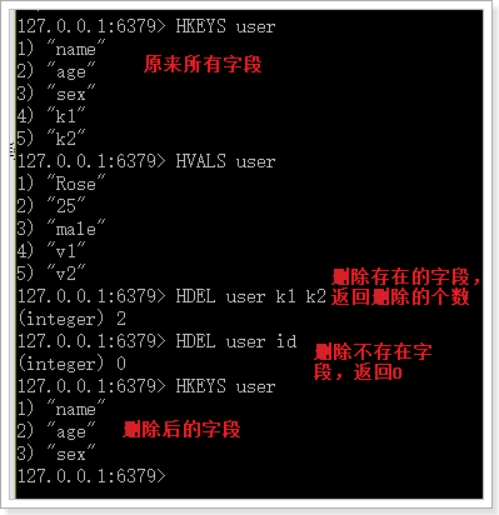
HKEYS
示例:
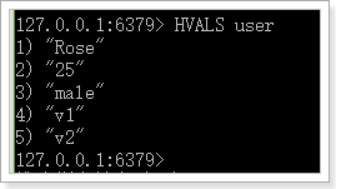
HVALS
HDEL(删除)
Hdel 命令用于删除哈希表 key 中的一个或多个指定字段,不存在的字段将被忽略。
2.4.Redis的持久化
Redis有两种持久化方案:RDB和AOF
2.4.1.RDB
触发条件
RDB是Redis的默认持久化方案,当满足一定的条件时,Redis会自动将内存中的数据全部持久化到硬盘。
条件在redis.conf文件中配置,格式如下:
当满足在time(单位是秒)时间内,至少进行了count次修改后,触发条件,进行RDB快照。
例如,默认的配置如下:

基本原理
RDB的流程是这样的:
- Redis使用fork函数来复制一份当前进程(父进程)的副本(子进程)
- 父进程继续接收并处理请求,子进程开始把内存中的数据写入硬盘中的临时文件
- 子进程写完后,会使用临时文件代替旧的RDB文件
2.4.2.AOF
基本原理
AOF方式默认是关闭的,需要修改配置来开启:
1
| appendonly yes # 把默认的no改成yes
|
AOF持久化的策略是,把每一条服务端接收到的写命令都记录下来,每隔一定时间后,写入硬盘的AOF文件中,当服务器重启后,重新执行这些命令,即可恢复数据。
AOF文件写入的频率是可以配置的:

AOF文件重写
当记录命令过多,必然会出现对同一个key的多次写操作,此时只需要记录最后一条即可,前面的记录都毫无意义了。因此,当满足一定条件时,Redis会对AOF文件进行重写,移除对同一个key的多次操作命令,保留最后一条。默认的触发条件:

主从
2.5.SpringDataRedis
之前,我们使用Redis都是采用的Jedis客户端,不过既然我们使用了SpringBoot,为什么不使用Spring对Redis封装的套件呢?
5.2.2.Spring Data Redis
官网:http://projects.spring.io/spring-data-redis/

Spring Data Redis,是Spring Data 家族的一部分。 对Jedis客户端进行了封装,与spring进行了整合。可以非常方便的来实现redis的配置和操作。
5.2.3.RedisTemplate基本操作
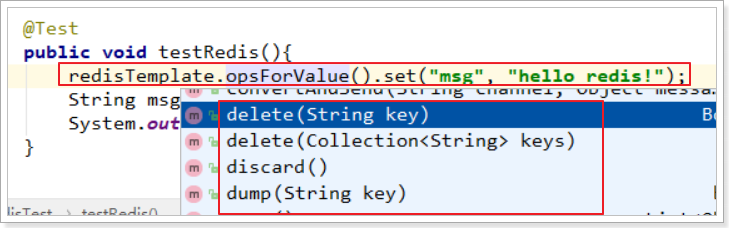
与以往学习的套件类似,Spring Data 为 Redis 提供了一个工具类:RedisTemplate。里面封装了对于Redis的五种数据结构的各种操作,包括:
- redisTemplate.opsForValue() :操作字符串
- redisTemplate.opsForHash() :操作hash
- redisTemplate.opsForList():操作list
- redisTemplate.opsForSet():操作set
- redisTemplate.opsForZSet():操作zset
例如我们对字符串操作比较熟悉的有:get、set等命令,这些方法都在 opsForValue()返回的对象中有:

其它一些通用命令,如del,可以通过redisTemplate.xx()来直接调用。
5.2.4.StringRedisTemplate
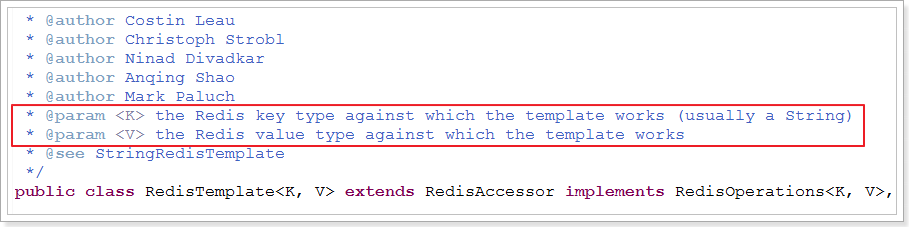
RedisTemplate在创建时,可以指定其泛型类型:
- K:代表key 的数据类型
- V: 代表value的数据类型
注意:这里的类型不是Redis中存储的数据类型,而是Java中的数据类型,RedisTemplate会自动将Java类型转为Redis支持的数据类型:字符串、字节、二二进制等等。
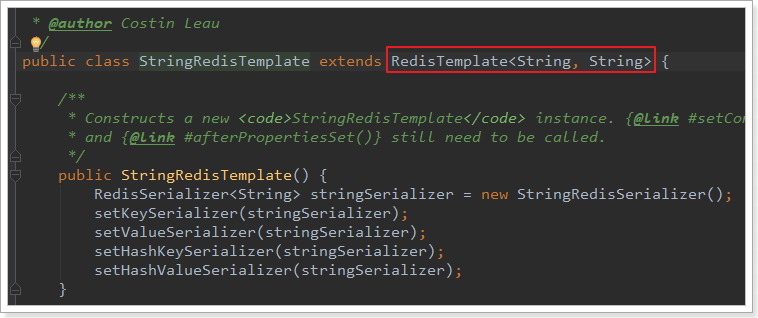
不过RedisTemplate默认会采用JDK自带的序列化(Serialize)来对对象进行转换。生成的数据十分庞大,因此一般我们都会指定key和value为String类型,这样就由我们自己把对象序列化为json字符串来存储即可。
因为大部分情况下,我们都会使用key和value都为String的RedisTemplate,因此Spring就默认提供了这样一个实现:
5.2.5.测试
我们新建一个测试项目,然后在项目中引入Redis启动器:
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
然后在配置文件中指定Redis地址:
1
2
3
| spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.206.66
|
然后就可以直接注入StringRedisTemplate对象了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = LyUserService.class)
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void testRedis() {
this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key1", "value1");
String val = this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key1");
System.out.println("val = " + val);
}
@Test
public void testRedis2() {
this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key2", "value2",
5, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
@Test
public void testHash(){
BoundHashOperations<String, Object, Object> hashOps =
this.redisTemplate.boundHashOps("user");
hashOps.put("name", "jack");
hashOps.put("age", "21");
Object name = hashOps.get("name");
System.out.println("name = " + name);
Map<Object, Object> map = hashOps.entries();
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> me : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(me.getKey() + " : " + me.getValue());
}
}
}
|
3.阿里短信服务
3.1.demo
注册页面上有短信发送的按钮,当用户点击发送短信,我们需要生成验证码,发送给用户。我们将使用阿里提供的阿里大于来实现短信发送。
参考课前资料的《阿里短信.md》学习demo入门
3.2.创建短信微服务
因为系统中不止注册一个地方需要短信发送,因此我们将短信发送抽取为微服务:ly-sms,凡是需要的地方都可以使用。
另外,因为短信发送API调用时长的不确定性,为了提高程序的响应速度,短信发送我们都将采用异步发送方式,即:
- 短信服务监听MQ消息,收到消息后发送短信。
- 其它服务要发送短信时,通过MQ通知短信微服务。
3.2.1.创建module
3.2.2.pom
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>leyou</artifactId>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>ly-sms</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-java-sdk-core</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.leyou</groupId>
<artifactId>ly-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
3.2.3.编写启动类
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class LySmsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LySmsApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
3.2.4.编写application.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| server:
port: 8086
spring:
application:
name: sms-service
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.206.66
username: leyou
password: leyou
virtual-host: /leyou
|
3.3.编写短信工具类
3.3.1.属性抽取
我们首先把一些常量抽取到application.yml中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| ly:
sms:
accessKeyID: LTAIfmmL26haCK0b
accessKeySecret: pX3RQns9ZwXs75M6Isae9sMgBLXDfY
signName: 乐优商城
verifyCodeTemplate: SMS_133976814
domain: dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com
action: SendSMS
version: 2017-05-25
regionID: cn-hangzhou
|
然后注入到属性类中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package com.leyou.sms.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ly.sms")
public class SmsProperties {
String accessKeyID;
String accessKeySecret;
String signName;
String verifyCodeTemplate;
String domain;
String version;
String action;
String regionID;
}
|
3.3.2.阿里客户端
首先,把发请求需要的客户端注册到Spring容器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package com.leyou.sms.config;
import com.aliyuncs.DefaultAcsClient;
import com.aliyuncs.IAcsClient;
import com.aliyuncs.profile.DefaultProfile;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SmsProperties.class)
public class SmsConfiguration {
@Bean
public IAcsClient acsClient(SmsProperties prop){
DefaultProfile profile = DefaultProfile.getProfile(
prop.getRegionID(), prop.getAccessKeyID(), prop.getAccessKeySecret());
return new DefaultAcsClient(profile);
}
}
|
3.3.2.工具类
我们把阿里提供的demo进行简化和抽取,封装一个工具类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| package com.leyou.sms.utils;
import com.aliyuncs.CommonRequest;
import com.aliyuncs.CommonResponse;
import com.aliyuncs.IAcsClient;
import com.aliyuncs.exceptions.ClientException;
import com.aliyuncs.exceptions.ServerException;
import com.aliyuncs.http.MethodType;
import com.aliyuncs.http.ProtocolType;
import com.leyou.common.enums.ExceptionEnum;
import com.leyou.common.exceptions.LyException;
import com.leyou.common.utils.JsonUtils;
import com.leyou.sms.config.SmsProperties;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
import static com.leyou.sms.constants.SmsConstants.*;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SmsHelper {
private IAcsClient client;
private SmsProperties prop;
public SmsHelper(IAcsClient client, SmsProperties prop) {
this.client = client;
this.prop = prop;
}
public void sendMessage(String phone, String signName, String template, String param) {
CommonRequest request = new CommonRequest();
request.setProtocol(ProtocolType.HTTPS);
request.setMethod(MethodType.POST);
request.setDomain(prop.getDomain());
request.setVersion(prop.getVersion());
request.setAction(prop.getAction());
request.putQueryParameter(SMS_PARAM_KEY_PHONE, phone);
request.putQueryParameter(SMS_PARAM_KEY_SIGN_NAME, signName);
request.putQueryParameter(SMS_PARAM_KEY_TEMPLATE_CODE, template);
request.putQueryParameter(SMS_PARAM_KEY_TEMPLATE_PARAM, param);
try {
CommonResponse response = client.getCommonResponse(request);
if(response.getHttpStatus() >= 300){
log.error("【SMS服务】发送短信失败。响应信息:{}", response.getData());
}
Map<String, String> resp = JsonUtils.toMap(response.getData(), String.class, String.class);
if(!StringUtils.equals(OK, resp.get(SMS_RESPONSE_KEY_CODE))){
log.error("【SMS服务】发送短信失败,原因{}", resp.get(SMS_RESPONSE_KEY_MESSAGE));
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.SEND_MESSAGE_ERROR);
}
log.info("【SMS服务】发送短信成功,手机号:{}, 响应:{}", phone, response.getData());
} catch (ServerException e) {
log.error("【SMS服务】发送短信失败,服务端异常。", e);
} catch (ClientException e) {
log.error("【SMS服务】发送短信失败,客户端异常。", e);
}
}
}
|
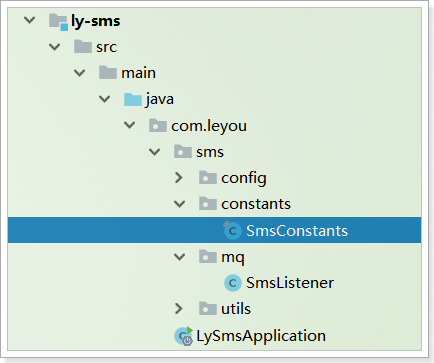
这里把阿里SDK中会用到的一些参数KEY,响应KEY都定义成了常量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public final class SmsConstants {
public static final String SMS_PARAM_KEY_PHONE = "PhoneNumbers";
public static final String SMS_PARAM_KEY_SIGN_NAME = "SignName";
public static final String SMS_PARAM_KEY_TEMPLATE_CODE = "TemplateCode";
public static final String SMS_PARAM_KEY_TEMPLATE_PARAM= "TemplateParam";
public static final String SMS_RESPONSE_KEY_CODE = "Code";
public static final String SMS_RESPONSE_KEY_MESSAGE = "Message";
public static final String OK = "OK";
}
|
如图:
3.4.编写消息监听器
接下来,编写消息监听器,当接收到消息后,我们发送短信。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| package com.leyou.sms.mq;
import com.leyou.common.exceptions.LyException;
import com.leyou.common.utils.JsonUtils;
import com.leyou.sms.config.SmsProperties;
import com.leyou.sms.utils.SmsHelper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Exchange.SMS_EXCHANGE_NAME;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.Queue.SMS_VERIFY_CODE_QUEUE;
import static com.leyou.common.constants.MQConstants.RoutingKey.VERIFY_CODE_KEY;
@Slf4j
@Component
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SmsProperties.class)
public class SmsListener {
@Autowired
private SmsProperties prop;
@Autowired
private SmsHelper smsHelper;
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = SMS_VERIFY_CODE_QUEUE),
exchange = @Exchange(name = SMS_EXCHANGE_NAME, type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = VERIFY_CODE_KEY
))
public void listenVerifyCode(Map<String, String> msg) {
if (msg == null) {
return;
}
String phone = msg.remove("phone");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(phone)) {
return;
}
try {
smsHelper.sendMessage(phone, prop.getSignName(), prop.getVerifyCodeTemplate(), JsonUtils.toString(msg));
} catch (LyException e) {
log.error("【SMS服务】短信验证码发送失败", e);
}
}
}
|
我们注意到,消息体是一个Map,里面有两个属性:
不要忘了,几个队列和交换机的名称,定义到ly-common中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.leyou.common.constants;
public abstract class MQConstants {
public static final class Exchange {
public static final String SMS_EXCHANGE_NAME = "ly.sms.exchange";
}
public static final class RoutingKey {
public static final String VERIFY_CODE_KEY = "sms.verify.code";
}
public static final class Queue{
public static final String SMS_VERIFY_CODE_QUEUE = "sms.verify.code.queue";
}
}
|
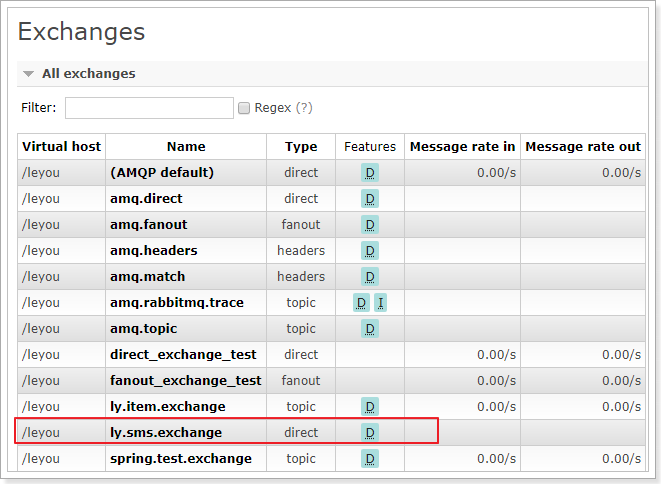
3.5.启动
启动项目,然后查看RabbitMQ控制台,发现交换机已经创建:
3.6.单元测试
编写一个测试类,尝试发送一条短信消息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SmsTest {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Test
public void testSendMessage() throws InterruptedException {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("phone", "130000000000");
map.put("code", "123321");
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("ly.sms.exchange", "sms.verify.code", map);
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
|